NumPy: numpy.full() function
numpy.full() function
The numpy.full() function is used to create a new array of the specified shape and type, filled with a specified value.
Syntax:
numpy.full(shape, fill_value, dtype=None, order='C')
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| shape | Shape of the new array, e.g., (2, 3) or 2. | Required |
| fill_value | Fill value. | Required |
| dtype | The desired data-type for the array The default, None, means np.array(fill_value).dtype. | optional |
| order | Whether to store multidimensional data in C- or Fortran-contiguous (row- or column-wise) order in memory | optional |
Return value:
[ndarray] Array of fill_value with the given shape, dtype, and order.
Example: Create arrays filled with a constant value using numpy.full()
>>> import numpy as np
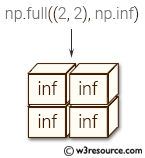
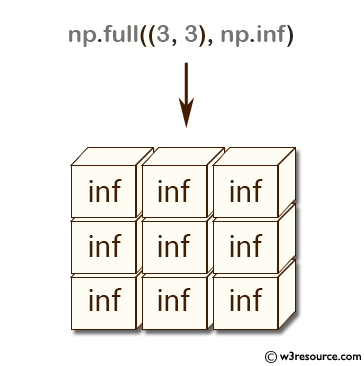
>>> np.full((3, 3), np.inf)
array([[ inf, inf, inf],
[ inf, inf, inf],
[ inf, inf, inf]])
>>> np.full((3, 3), 10.1)
array([[ 10.1, 10.1, 10.1],
[ 10.1, 10.1, 10.1],
[ 10.1, 10.1, 10.1]])
The above code creates arrays filled with a constant value using the numpy.full() function. In the first example, np.full((3, 3), np.inf) creates a 3x3 numpy array filled with np.inf (infinity). np.inf is a special floating-point value that represents infinity, and is often used in calculations involving limits and asymptotes.
In the second example, np.full((3, 3), 10.1) creates a 3x3 numpy array filled with the value 10.1. Here, the dtype parameter is omitted, so numpy infers the data type of the array from the given value.
Visual Presentation:
Example: Create an array filled with a single value using np.full()
>>> import numpy as np
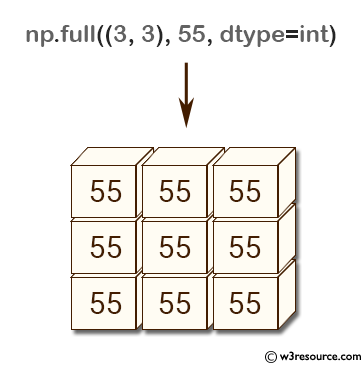
>>> np.full((3,3), 55, dtype=int)
array([[55, 55, 55],
[55, 55, 55],
[55, 55, 55]])
In the above code, np.full((3,3), 55, dtype=int) creates a 3x3 numpy array filled with the integer value 55. The dtype parameter is explicitly set to int, so the resulting array has integer data type.
Visual Presentation:
Frequently asked questions (FAQ) - numpy. full ()
1. What does numpy.full() do?
The numpy.full() function creates a new array of a specified shape and fills it with a specified value.
2. When should I use numpy.full()?
Use numpy.full() when you need an array of a certain shape that is entirely filled with the same value, which can be useful for initializing arrays for further computations.
3. How is numpy.full() different from numpy.zeros() and numpy.ones()?
While numpy.zeros() creates an array filled with zeros and numpy.ones() creates an array filled with ones, numpy.full() allows you to specify any fill value for the array.
4. What data types does numpy.full() support?
numpy.full() supports all standard NumPy data types, including integers, floats, and complex numbers. You can also specify the data type explicitly if needed.
5 Can numpy.full() create arrays with custom shapes?
Yes, numpy.full() can create arrays of any shape, including multi-dimensional arrays.
6. Is it possible to create an array with uninitialized values using numpy.full()?
No, numpy.full() always initializes the array with the specified fill value. For uninitialized values, use numpy.empty() instead.
7. Can I use numpy.full() with NumPy's broadcasting?
No, numpy.full() does not utilize broadcasting when creating the array. It directly fills the array with the specified value.
8. What are some common use cases for numpy.full()?
Common use cases include:
- Initializing arrays with a specific default value.
- Creating masks or grids for computational purposes.
- Setting up arrays for testing algorithms with known values.
9. How can we ensure the array created by numpy.full() is contiguous in memory?
By default, arrays created by numpy.full() are contiguous in memory. However, you can explicitly check the array's memory layout using array.flags.
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous: zeros_like()
Next: full_like()
