NumPy: numpy.diag() function
numpy.diag() function
The numpy.diag() function creates a diagonal matrix or extracts the diagonal elements of a matrix. It can also construct a diagonal array from a one-dimensional array.
Syntax:
numpy.diag(v, k=0)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| v | If v is a 2-D array, the function returns a copy of its k-th diagonal. If v is a 1-D array, it returns a 2-D array with v on the k-th diagonal. | Required |
| k | Specifies the diagonal in question. The default is 0, which corresponds to the main diagonal. Use k > 0 for diagonals above the main diagonal, and k < 0 for diagonals below the main diagonal. | Optional |
Return value:
out : ndarray - The extracted diagonal or constructed diagonal array.
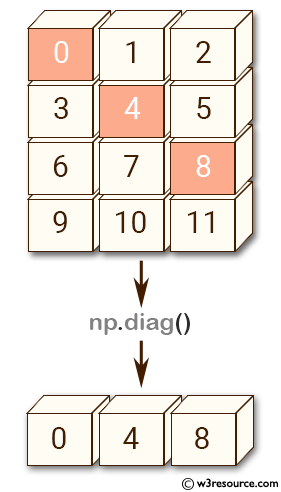
Example: Extracting Diagonal Elements from a Matrix
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(12).reshape((4, 3))
print(np.diag(a))
Output:
[0 4 8]
In this example, a 4x3 matrix a is created using arange() and reshape(). The diag() function extracts the main diagonal elements of a.
Visual Presentation:
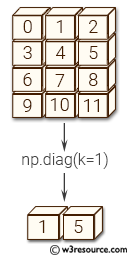
Example: Extracting Diagonal Elements with an Offset
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(12).reshape((4, 3))
print(np.diag(a, k=1))
Output:
[1 5]
Here, the diag() function extracts elements from the diagonal above the main diagonal (offset by 1).
Visual Presentation:
Example: Extracting a Subdiagonal
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(12).reshape((4, 3))
print(np.diag(a, k=-1))
Output:
[ 3 7 11]
In this example, the diag() function extracts elements from the diagonal below the main diagonal (offset by -1).
Example: Creating a Diagonal Matrix from a 1D Array
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(np.diag(a))
Output:
[[1 0 0] [0 2 0] [0 0 3]]
This example demonstrates creating a diagonal matrix from a one-dimensional array a.
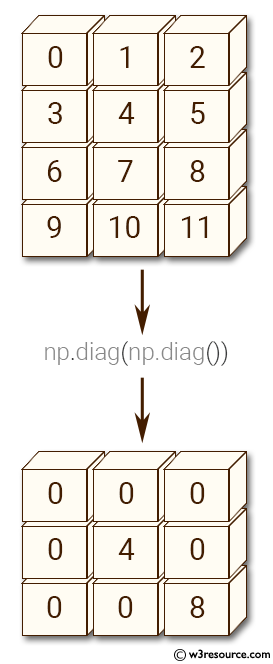
Example: Creating a Diagonal Matrix from the Diagonal of Another Matrix
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(12).reshape((4, 3))
print(np.diag(np.diag(a)))
Output:
[[0 0 0] [0 4 0] [0 0 8]]
Here, the diagonal elements of matrix a are extracted and then used to create a new diagonal matrix.
Visual Presentation:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): numpy. diag() Function
1. What does the numpy.diag() function do?
The numpy.diag() function creates a diagonal matrix from a 1-D array or extracts the diagonal elements from a 2-D array.
2. Can numpy.diag() handle both 1-D and 2-D arrays?
Yes, numpy.diag() can take a 1-D array to create a diagonal matrix or a 2-D array to extract its diagonal elements.
3. What happens if I provide a 2-D array to numpy.diag()?
If a 2-D array is provided, numpy.diag() extracts and returns the elements from the specified diagonal of the array.
4. What does the k parameter in numpy.diag() specify?
The k parameter specifies which diagonal to consider. k=0 refers to the main diagonal, k>0 for diagonals above it, and k<0 for diagonals below it.
5. Can numpy.diag() create matrices with non-zero elements off the main diagonal?
No, numpy.diag() only creates diagonal matrices with non-zero elements on the specified diagonal. All off-diagonal elements are zero.
6. Is the original array modified when using numpy.diag()?
No, numpy.diag() does not modify the original array; it returns a new array with the specified diagonal elements.
7. What is returned when a 1-D array is passed to numpy.diag()?
When a 1-D array is passed, numpy.diag() returns a 2-D diagonal matrix with the elements of the 1-D array on the main diagonal.
8. Can numpy.diag() extract subdiagonals or superdiagonals?
Yes, by adjusting the k parameter, numpy.diag() can extract subdiagonals (k<0) or superdiagonals (k>0).
9. What type of array does numpy.diag() return?
numpy.diag() returns an ndarray, either a 1-D array of diagonal elements or a 2-D diagonal matrix, depending on the input.
10. Why would I use numpy.diag() in my computations?
numpy.diag() is useful for creating diagonal matrices for linear algebra operations, extracting diagonal elements for analysis, and constructing matrices with specified diagonal values.
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous: ogrid()
Next: diagflat()
