NumPy: numpy.diagflat() function
numpy.diagflat() function
The numpy.diagflat() function is used to create a two-dimensional array with the flattened input as a diagonal.
Syntax:
numpy.diagflat(v, k=0)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| v | Input data, which is flattened and set as the k-th diagonal of the output. | Required |
| k | Diagonal to set; 0, the default, corresponds to the 'main' diagonal, a positive (negative) k giving the number of the diagonal above (below) the main. | optional |
Return value:
The 2-D output array.
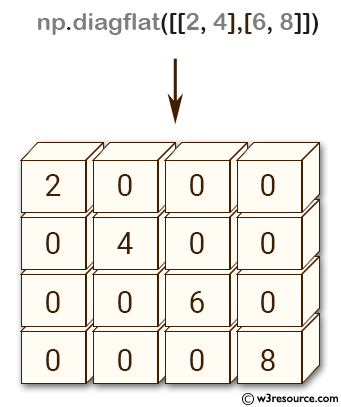
Example: Creating a diagonal array using diagflat()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.diagflat([[2,4], [6,8]])
array([[2, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 4, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 6, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 8]])
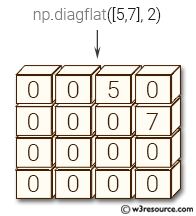
The above code creates a diagonal array using the diagflat() function in NumPy. The diagflat() function creates a 2-D array with the input array as its diagonal. Here the input array is [[2, 4], [6, 8]], which has two rows and two columns. The resulting diagonal array has four rows and four columns, with the diagonal elements of the input array on the main diagonal of the output array.
Pictorial Presentation:
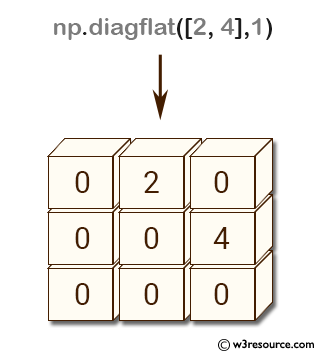
Example: Creating a diagonal array with an offset using np.diagflat()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.diagflat([2,4], 1)
array([[0, 2, 0],
[0, 0, 4],
[0, 0, 0]])
The above code uses the np.diagflat() function to create a diagonal array with an offset. The function takes an input argument, which is a list or an array of numbers that will be placed on the diagonal of the resulting array. The second argument is an integer that specifies the offset of the diagonal.
Here, the input array is [2,4] and the offset is 1. Therefore, the resulting array will have [2,4] on the first diagonal above the main diagonal, and all other elements will be zero. The shape of the array is determined automatically based on the input array and offset.
Pictorial Presentation:
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
