NumPy: numpy.mgrid() function
numpy.mgrid() function
The numpy.mgrid() function is used to get a dense multi-dimensional 'meshgrid'.
An instance of numpy.lib.index_tricks.nd_grid which returns an dense (or fleshed out) mesh-grid when indexed, so that each returned argument has the same shape. The dimensions and number of the output arrays are equal to the number of indexing dimensions. If the step length is not a complex number, then the stop is not inclusive.
However, if the step length is a complex number (e.g. 5j), then the integer part of its magnitude is interpreted as specifying the number of points to create between the start and stop values, where the stop value is inclusive.
Syntax:
numpy.mgrid = <numpy.lib.index_tricks.nd_grid object>
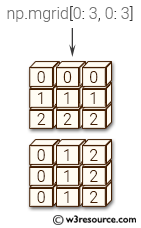
Return value:
mesh-grid 'ndarrays' all of the same dimensions.
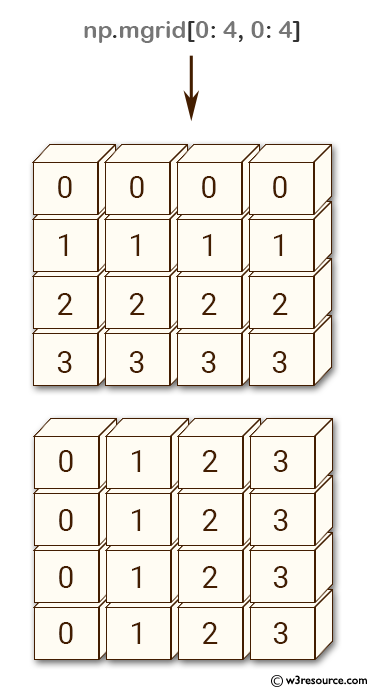
Example: Creating a Mesh Grid using np.mgrid
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.mgrid[0:4, 0:4]
array([[[0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3, 3]],
[[0, 1, 2, 3],
[0, 1, 2, 3],
[0, 1, 2, 3],
[0, 1, 2, 3]]])
The above code demonstrates how to create a 2-dimensional mesh grid using the np.mgrid function from the NumPy library. The function takes as input the slicing ranges for each dimension and returns a dense grid with the same shape as the input slices.
In this case, np.mgrid[0:4, 0:4] creates a 2D grid with 4 rows and 4 columns, where the first row is filled with zeros, the second with ones, and so on. The second row is filled with 0, 1, 2, and 3, repeating for each column. The resulting array is a 3D array with shape (2,4,4).
Pictorial Presentation:
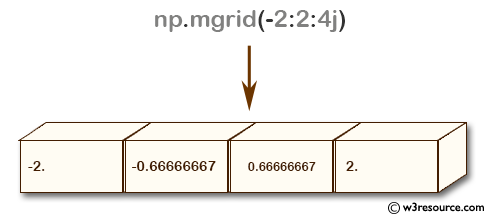
Example: Creating a grid array with evenly spaced values
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.mgrid[-2:2:4j]
array([-2. , -0.66666667, 0.66666667, 2. ])
The above code creates an evenly spaced 1-dimensional array with 4 elements ranging from -2 to 2. The parameters to mgrid specify the start and end of the range, and the number of elements to create in the range. In this case, the range is from -2 to 2, with 4 elements, and 4j is used to indicate that a complex step size of (4-1)j/4 is to be used to ensure that the endpoint is included. The resulting array is a 1-dimensional array with 4 elements.
Pictorial Presentation:
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous: meshgrid()
Next: ogrid()
