NumPy: numpy.zeros() function
numpy.zeros() function
The numpy.zeros() function is used to create an array of specified shape and data type, filled with zeros.
The function is commonly used to initialize an array of a specific size and type, before filling it with actual values obtained from some calculations or data sources. It is also used as a placeholder to allocate memory for later use.
Syntax:
numpy.zeros(a, dtype=None, order='K', subok=True)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| shape | Defines the shape of the new array, e.g., (2, 3) or 2. | Required |
| dtype | Specifies the desired data type for the array, e.g., numpy.int8. The default is numpy.float64. | Optional |
| order | Memory layout order: 'C' for row-major (C-style), 'F' for column-major (Fortran-style). Default is 'C'. | Optional |
| subok | If True, subclasses are passed through; otherwise, the returned array will be forced to be a base-class array. Default is True. | Optional |
Return value:
Returns an ndarray of zeros with the specified shape, data type, and memory layout order.
Example 1: Creating a 2D array of zeros
Code:
import numpy as np
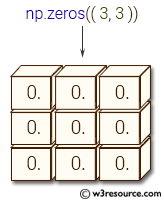
a = (3, 2)
array = np.zeros(a)
print(array)
Output:
[[0. 0.] [0. 0.] [0. 0.]]
In this example, a tuple (3, 2) defines the shape of the array, and np.zeros() creates a 2D array filled with zeros.
Visual Presentation:
Example 2: Creating a 1D array of zeros
Code:
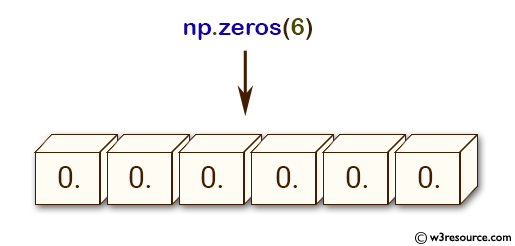
import numpy as np
array = np.zeros(6)
print(array)
Output:
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
Creates a one-dimensional array of size 6 with all elements set to 0, with a default data type of float.
Example 3: Specifying data type for zeros array
Code:
import numpy as np
array = np.zeros((6,), dtype=int)
print(array)
Output:
[0 0 0 0 0 0]
Creates a one-dimensional array of size 6 with all elements set to 0, and the data type is integer.
Visual Presentation:
Example 4: Creating a 3D array with specific values on one axis
Code:
import numpy as np
nums = np.zeros((2, 3, 4), dtype=int)
nums[:, 1, :] = 2
print(nums)
Output:
[[[0 0 0 0] [2 2 2 2] [0 0 0 0]] [[0 0 0 0] [2 2 2 2] [0 0 0 0]]]
Creates a 3D array with dimensions (2, 3, 4) and sets the values along the second axis to 2.
Example 5: Creating a 2D array with a custom data type and byte order
Code:
import numpy as np
nums = np.zeros((2, 3), dtype=np.dtype('>u2'))
print(nums)
Output:
[[0 0 0] [0 0 0]]
Creates a 2D array with dimensions (2, 3) using an unsigned 16-bit integer with big-endian byte order.
Frequently Asked Questions: numpy.zeros() Function
1. What is the purpose of the numpy.zeros() function?
The numpy.zeros() function is used to create a new array of given shape and type, filled with zeros. It's useful for initializing arrays before performing calculations or storing data.
2. How do I specify the shape of the array I want to create?
You specify the shape using a tuple, e.g., (3, 2) for a 3x2 array or 5 for a one-dimensional array with 5 elements.
3. What data type does the array default to if I don't specify one?
If not specified, the default data type is numpy.float64.
4. Can I create arrays with different data types?
Yes, you can specify the dtype parameter to create arrays of different data types, such as numpy.int32, numpy.float32, or even custom types.
5. How do I control the memory layout of the array?
Use the order parameter to specify 'C' for row-major (C-style) order or 'F' for column-major (Fortran-style) order.
6. Can I create multi-dimensional arrays with numpy.zeros()?
Yes, you can create multi-dimensional arrays by providing the appropriate shape tuple, such as (2, 3, 4) for a 3D array.
7. What does the subok parameter do?
The subok parameter, if set to True, allows the creation of arrays using subclasses of ndarray. If False, the result will always be a base-class array.
8. Is it possible to create an empty array using numpy.zeros()?
While numpy.zeros() fills the array with zeros, if you need an uninitialized array, you can use numpy.empty() instead.
9. Can I use numpy.zeros() to initialize arrays for later use in algorithms?
Yes, initializing arrays with numpy.zeros() is a common practice in algorithms that require pre-allocated space for results or intermediate values.
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous: ones_like()
Next: zeros_like()
