MySQL DATE() function
DATE() function
MySQL DATE() takes the DATE part out from a datetime expression. It's particularly useful for situations where you want to work with dates separately from the time component.
This function is useful in -
- By using the DATE() function, you can perform date-based comparisons without considering the time component.
- When grouping and aggregating data by date, the DATE() function helps ensure accurate grouping by extracting the date part from datetime values.
- In reporting scenarios, DATE() can be used to extract dates for more organized and readable reports, without the clutter of time information.
- When integrating data from MySQL with other systems or applications, the DATE() function ensures that only the date part is used, preventing conflicts due to time zone differences.
- By using DATE() in filtering or joining conditions, you can optimize queries that involve datetime values, as the comparison considers dates only.
- For graphical representations such as charts or graphs, using DATE() helps label data points with dates only, enhancing clarity.
Syntax:
DATE(expr);
Where expr is a datetime.
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
Pictorial Presentation:
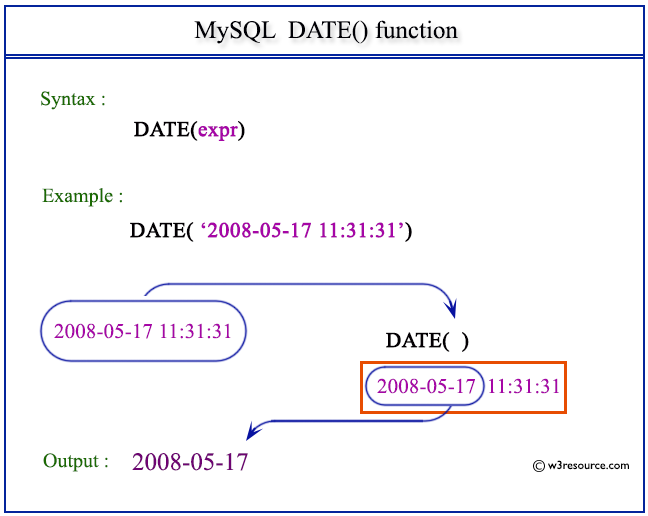
Example: MySQL DATE() function
The following statement will extract the DATE portion from the specified daetime 2008-05-17 11:31:31.
Code:
SELECT DATE('2008-05-17 11:31:31') as required_DATE;
Output:
mysql> SELECT DATE('2008-05-17 11:31:31') as required_DATE;
+---------------+
| required_DATE |
+---------------+
| 2008-05-17 |
+---------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Video Presentation:
All Date and Time Functions :
Click here to see the MySQL Date and time functions.
Previous: DATE_SUB()
Next: DATEDIFF()
