MySQL DATE_FORMAT() function
DATE_FORMAT() function
Introduction:
In data-driven applications, dates often need to be displayed in formats that are easy for users to understand and that align with their locale preferences. MySQL’s DATE_FORMAT() function provides a powerful way to achieve this. It transforms dates from raw storage format into user-friendly representations.
What is MySQL DATE_FORMAT()?
The DATE_FORMAT() function in MySQL allows you to format a date according to the specified format string. This function is incredibly versatile, enabling you to present date and time information in a wide array of formats that suit different requirements, whether for user interfaces, data exports, or internationalization.
This function is useful in -
- The primary purpose of the DATE_FORMAT() function is to allow you to customize the way date and datetime values are displayed.
- In graphical user interfaces (GUIs), DATE_FORMAT() helps display dates in formats that match the UI design, creating a cohesive user experience.
- DATE_FORMAT() is essential for filtering and sorting date-based data in specific formats, ensuring accurate comparisons and ordering.
- In applications that are used in different countries, DATE_FORMAT() helps adapt date representations to the local date format conventions.
- When exporting or importing data to/from external systems, DATE_FORMAT() ensures that the date format is consistent with the target system's requirements.
- DATE_FORMAT() is used to format dates in a way that is familiar to users based on their cultural or regional preferences.
Syntax:
DATE_FORMAT(date,format)
Arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| date | A date. |
| format | Indicates how to format a date. |
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
Below are the specifiers we can use to format dates. Each specifier must be prefixed with a %.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| %a | Abbreviated weekday name (Sun..Sat) |
| %b | Abbreviated month name (Jan..Dec) |
| %c | Month, numeric (0..12) |
| %D | Day of the month with English suffix (0th, 1st, 2nd, 3rd, …) |
| %d | Day of the month, numeric (00..31) |
| %e | Day of the month, numeric (0..31) |
| %f | Microseconds (000000..999999) |
| %H | Hour (00..23) |
| %h | Hour (01..12) |
| %I | Hour (01..12) |
| %i | Minutes, numeric (00..59) |
| %j | Day of year (001..366) |
| %k | Hour (0..23) |
| %l | Hour (1..12) |
| %M | Month name (January..December) |
| %m | Month, numeric (00..12) |
| %p | AM or PM |
| %r | Time, 12-hour (hh:mm:ss followed by AM or PM) |
| %S | Seconds (00..59) |
| %s | Seconds (00..59) |
| %T | Time, 24-hour (hh:mm:ss) |
| %U | Week (00..53), where Sunday is the first day of the week |
| %u | Week (00..53), where Monday is the first day of the week |
| %V | Week (01..53), where Sunday is the first day of the week; used with %X |
| %v | Week (01..53), where Monday is the first day of the week; used with %x |
| %W | Weekday name (Sunday..Saturday) |
| %w | Day of the week (0=Sunday..6=Saturday) |
| %X | Year for the week where Sunday is the first day of the week, numeric, four digits; used with %V |
| %x | Year for the week, where Monday is the first day of the week, numeric, four digits; used with %v |
| %Y | Year, numeric, four digits |
| %y | Year, numeric (two digits) |
| %% | A literal “%” character |
| %x | x, for any “x” not listed above |
Visual Presentation:
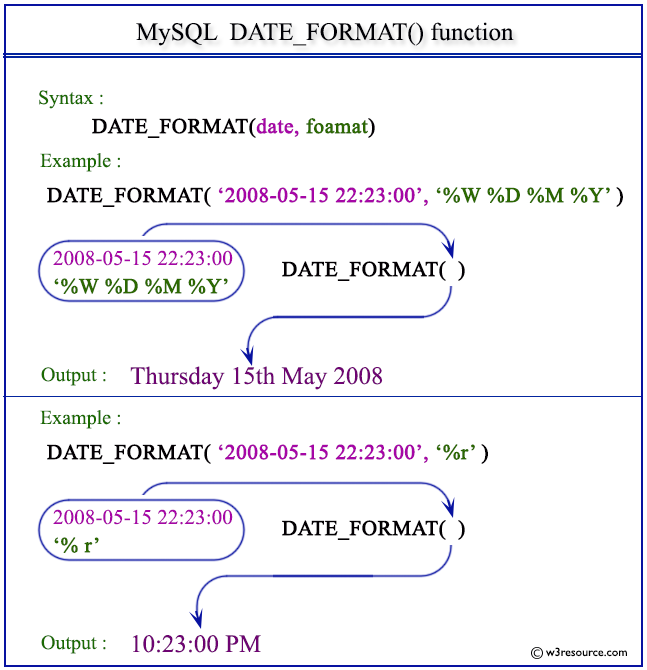
Example: MySQL DATE_FORMAT() function
select date_format(date, '%a %D %b %Y')
as formatted_date
from table_name;
Where date is the name of your date field, and formatted_date is a column alias which you can use as a column heading.
| Example Date: 11th February 2011 Replace date with the name of your date field... |
|
| date_format String | Example |
|---|---|
| '%Y-%m-%d' | 2011-02-11 |
| '%e/%c/%Y' | 11/2/2011 UK |
| '%c/%e/%Y' | 2/11/2011 US |
| '%d/%m/%Y' | 11/02/2011 UK |
| '%m/%d/%Y' | 02/11/2011 US |
| '%e/%c/%Y %H:%i' | 11/2/2011 12:30 UK |
| '%c/%e/%Y %H:%i' | 2/11/2011 12:30 US |
| '%d/%m/%Y %H:%i' | 11/02/2011 12:30 UK |
| '%m/%d/%Y %H:%i' | 02/11/2011 12:30 US |
| '%e/%c/%Y %T' | 11/2/2011 12:30:10 UK |
| '%c/%e/%Y %T' | 2/11/2011 12:30:10 US |
| '%d/%m/%Y %T' | 11/02/2011 12:30:10 UK |
| '%m/%d/%Y %T' | 02/11/2011 12:30:10 US |
| '%a %D %b %Y' | Fri 11th Feb 2011 |
| '%a %D %b %Y %H:%i' | Fri 11th Feb 2011 12:30 |
| '%a %D %b %Y %T' | Fri 11th Feb 2011 12:30:10 |
| '%a %b %e %Y' | Fri Feb 11 2011 |
| '%a %b %e %Y %H:%i' | Fri Feb 11 2011 12:30 |
| '%a %b %e %Y %T' | Fri Feb 11 2011 12:30:10 |
| '%W %D %M %Y' | Friday 11th February 2011 |
| '%W %D %M %Y %H:%i' | Friday 11th February 2011 12:30 |
| '%W %D %M %Y %T' | Friday 11th February 2011 12:30:10 |
| '%l:%i %p %b %e, %Y' | 12:30 PM Feb 11, 2011 |
| '%M %e, %Y' | February 11, 2011 |
Best Practices:
- Use Consistent Formats: Choose a consistent date format for your application to avoid confusion.
- Performance Considerations: Be mindful of the performance impact when using DATE_FORMAT() in large datasets. Pre-format dates if possible for frequently accessed data.
- Localization: Use DATE_FORMAT() to adapt your application’s date formats to the user's locale settings.
Potential Pitfalls:
- Format Mismatch: Ensure the format specifiers match the data type of the date value being formatted.
- Incorrect Output: Double-check the format string to avoid unexpected results, especially when dealing with time zones or international date formats.
The following statement will format the specified datetime 2008-05-15 22:23:00 according to the format specifier %W %D %M %Y. Here date has been formatted with week day name, day of the month with english suffix, month name and year in numeric.
Code:
SELECT
-- Format the given date and time using the specified pattern
DATE_FORMAT(
'2008-05-15 22:23:00', -- Input date/time
'%W %D %M %Y' -- Format pattern for the output
);
Explanation:
- SELECT:
- Initiates a query to retrieve data. Here, it’s used to return the formatted date result.
- DATE_FORMAT:
- MySQL function to format date/time values. Converts the input date 2008-05-15 22:23:00 into a specific string format.
- Format String ('%W %D %M %Y'):
- %W: Full weekday name (e.g., 'Thursday').
- %D: Day of the month with suffix (e.g., '15th').
- %M: Full month name (e.g., 'May').
- %Y: Four-digit year (e.g., '2008').
Output:
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2008-05-15 22:23:00', '%W %D %M %Y');
+---------------------------------------------------+
| DATE_FORMAT('2008-05-15 22:23:00', '%W %D %M %Y') |
+---------------------------------------------------+
| Thursday 15th May 2008 |
+---------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
Example: DATE_FORMAT() function with (%r) specifier
The following statement will format the specified datetime 2008-05-15 22:23:00 according to the format specifier %r. Here the function returns the time in 12-hour format followed by AM or PM.
Code:
SELECT
-- Apply the DATE_FORMAT function to format the given date and time
DATE_FORMAT(
-- Input date and time in the format 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'
'2008-05-15 22:23:00',
-- Format specifier for 12-hour time followed by AM/PM
'%r'
);
Explanation:
- SELECT: Initiates a query to retrieve data from the database.
- DATE_FORMAT: A MySQL function used to format date and time values according to a specified format.
- '2008-05-15 22:23:00': Represents the input date and time to be formatted, provided as a string in the format 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM '. This corresponds to May 15, 2008, at 10:23 PM (22:23 in 24-hour format).
- '%r': Format specifier used within the DATE_FORMAT function. %r is a format code representing 12-hour time with AM/PM indicator.
Output:
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2008-05-15 22:23:00', '%r');
+------------------------------------------+
| DATE_FORMAT('2008-05-15 22:23:00', '%r') |
+------------------------------------------+
| 10:23:00 PM |
+------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: DATE_FORMAT() function using table
The following statement will format the specified ‘ord_date’ column from purchase table according to the format specifier %W %D %M %Y and display all the rows.
Sample table: purchase
Code:
SELECT
invoice_no, -- Select the invoice number
ord_date, -- Select the original order date
DATE_FORMAT(ord_date,'%W %D %M %Y') -- Format the order date with the specified format
FROM
purchase; -- Select data from the 'purchase' table
Explanation:
- SELECT: Initiates a query to retrieve data from the database. Specifies the columns to be included in the result set.
- invoice_no: Selects the column storing the invoice numbers.
- ord_date: Selects the column storing the original order dates.
- DATE_FORMAT(ord_date,'%W %D %M %Y'): Utilizes the DATE_FORMAT function to format the ord_date column.
- %W: Full weekday name (e.g., 'Thursday').
- %D: Day of the month with suffix (e.g., '15th').
- %M: Full month name (e.g., 'May').
- %Y: Four-digit year (e.g., '2008').
- This formats the original order date in a more readable format, combining the weekday, day, month, and year.
- FROM purchase;: Specifies the table from which data will be retrieved, in this case, the 'purchase' table.
Output:
mysql> SELECT invoice_no,ord_date,DATE_FORMAT(ord_date,'%W %D %M %Y')
-> FROM purchase;
+------------+------------+-------------------------------------+
| invoice_no | ord_date | DATE_FORMAT(ord_date,'%W %D %M %Y') |
+------------+------------+-------------------------------------+
| INV0001 | 2008-07-06 | Sunday 6th July 2008 |
| INV0002 | 2008-08-09 | Saturday 9th August 2008 |
| INV0003 | 2008-09-15 | Monday 15th September 2008 |
| INV0004 | 2007-08-22 | Wednesday 22nd August 2007 |
| INV0005 | 2007-06-25 | Monday 25th June 2007 |
| INV0006 | 2007-09-20 | Thursday 20th September 2007 |
+------------+------------+-------------------------------------+
6 rows in set (0.09 sec)
Example: DATE_FORMAT() function with where
The following statement will format the specified ‘ord_date’ column from purchase table according to the format specifier %W %D %M %Y and returns those orders which had been placed after 2007.
Sample table: purchase
Code:
SELECT
invoice_no, -- Select the invoice number
ord_date, -- Select the original order date
DATE_FORMAT(ord_date,'%W %D %M %Y') -- Format the order date with the specified format
FROM
purchase -- Select data from the 'purchase' table
WHERE
DATE_FORMAT(ord_date,'%Y') > 2007; -- Filter rows where the year of the order date is greater than 2007
Explanation:
- SELECT: Initiates a query to retrieve data from the database. Specifies the columns to be included in the result set.
- invoice_no: Selects the column storing the invoice numbers.
- ord_date: Selects the column storing the original order dates.
- DATE_FORMAT(ord_date,'%W %D %M %Y'): Utilizes the DATE_FORMAT function to format the ord_date column.
- %W: Full weekday name (e.g., 'Thursday').
- %D: Day of the month with suffix (e.g., '15th').
- %M: Full month name (e.g., 'May').
- %Y: Four-digit year (e.g., '2008').
- This formats the original order date in a more readable format, combining the weekday, day, month, and year.
- FROM purchase: Specifies the table from which data will be retrieved, in this case, the 'purchase' table.
- WHERE: Filters the rows based on a condition.
- DATE_FORMAT(ord_date,'%Y') > 2007: Utilizes the DATE_FORMAT function to extract the year from the ord_date column. Compares the extracted year to 2007.
- Rows are filtered to include only those where the order date year is greater than 2007.
Output:
mysql> SELECT invoice_no,ord_date, DATE_FORMAT(ord_date,'%W %D %M %Y')
-> FROM purchase
-> WHERE DATE_FORMAT(ord_date,' %Y')>2007;
+------------+------------+-------------------------------------+
| invoice_no | ord_date | DATE_FORMAT(ord_date,'%W %D %M %Y') |
+------------+------------+-------------------------------------+
| INV0001 | 2008-07-06 | Sunday 6th July 2008 |
| INV0002 | 2008-08-09 | Saturday 9th August 2008 |
| INV0003 | 2008-09-15 | Monday 15th September 2008 |
+------------+------------+-------------------------------------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
Comparisons with Similar Functions:
While DATE_FORMAT() is specific to MySQL, other SQL databases have similar functions:
- PostgreSQL: TO_CHAR()
- SQL Server: FORMAT()
- SQLite: strftime()
These functions serve the same purpose but have different syntax and capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) - MySQL DATE_FORMAT() Function
1. What is MySQL DATE_FORMAT()?
MySQL DATE_FORMAT() is a function used to format date and datetime values into user-specified formats. It is commonly used to display dates in a readable manner according to application or user requirements.
2. Where is MySQL DATE_FORMAT() useful?
DATE_FORMAT() is essential for customizing the display of dates in applications, ensuring compatibility with graphical user interfaces (GUIs), facilitating data sorting and filtering based on date formats, and adapting date representations to different locale conventions.
3. What are the arguments of MySQL DATE_FORMAT()?
The function takes two arguments:
- date: The date or datetime value to be formatted.
- format: Specifies how the date should be formatted using various format specifiers (e.g., %Y for year, %m for month).
4. What are some best practices when using MySQL DATE_FORMAT()?
Best practices include maintaining consistent date formats across applications to avoid confusion, considering performance implications when formatting large datasets, and using DATE_FORMAT() to localize date formats based on user preferences.
5. Are there potential pitfalls to be aware of?
Common pitfalls include mismatched format specifiers that do not correspond to the date type being formatted, which can lead to incorrect outputs. Care should also be taken when handling time zones and international date formats to avoid unexpected results.
6. What are alternatives to MySQL DATE_FORMAT() in other SQL databases?
Similar functions in other databases include PostgreSQL's TO_CHAR(), SQL Server's FORMAT(), and SQLite's strftime(). These functions serve analogous purposes but have different syntax and capabilities compared to MySQL's DATE_FORMAT().
Video Presentation:
Click here to see the MySQL Date and time functions.
Previous: DATE_ADD()
Next: DATE_SUB()
