MySQL MAKEDATE() function
MAKEDATE() function
MySQL MAKEDATE() returns a date by taking a value of a year and a number of days. The number of days must be greater than 0 otherwise a NULL will be returned.
This function is useful in -
- MAKEDATE() is used to generate dates for specific occasions or events that occur on certain days of the year.
- MAKEDATE() is valuable for converting ordinal day numbers (1 to 366) within a year into full date values.
- In applications that require the initialization of date-related data, MAKEDATE() helps create initial date values.
- The function aids in generating date values for reports and data analysis based on specific years and days.
- When working with datasets that include year and day information, MAKEDATE() is used to generate full date values for further processing.
- MAKEDATE() can be used to represent historical dates with only the year and day information available.
- MAKEDATE() is used to create custom date representations for special purposes that do not follow the standard year-month-day format.
Syntax:
MAKEDATE(year,dayofyear);
Arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| year | Indicates a year. |
| dayofyear | An integer indicating days of a year. |
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
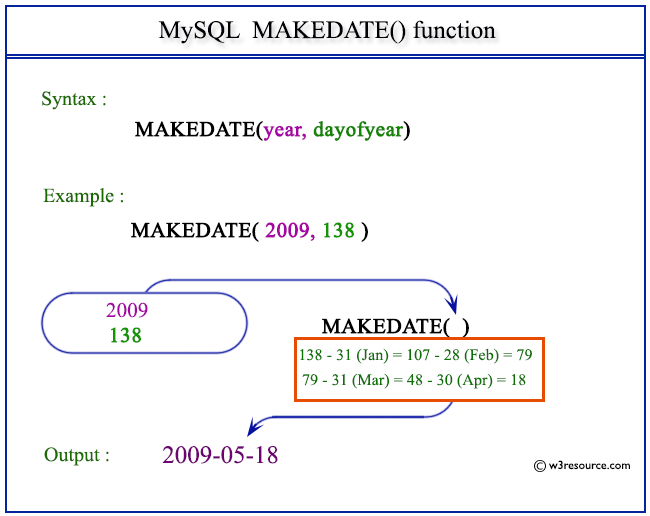
Pictorial Presentation:
Example: MySQL MAKEDATE() function
The following statement will make a date from the year 2009 and number of days 138.
Code:
SELECT MAKEDATE(2009,138);
Output:
mysql> SELECT MAKEDATE(2009,138); +--------------------+ | MAKEDATE(2009,138) | +--------------------+ | 2009-05-18 | +--------------------+ 1 row in set (0.03 sec)
Video Presentation:
Click here to see the MySQL Date and time functions.
Previous: LOCALTIMESTAMP()
Next: MAKETIME()
