PHP: get_html_ translation_ table() function
PHP: Convert special or all applicable characters to HTML entities
The get_html_translation_table() returns the translation table used by htmlspecialchars() function and htmlentities() function.
Version
(PHP 4 PHP 5 )
Syntax
get_html_translation_table(table, quote_style)
Parameters
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| table | For a given string, two constants either HTML_ENTITIES or HTML_SPECIALCHARS, defines what kind of character to html entities mapping is to be done. | Optional | Integer |
| quote_style | Refers to a style of encoding single and double quote. ENT_COMPAT : Only convert double quotes, leaving single quotes unaltered. This is the default one. ENT_QUOTES : Converts both single and double quotes. ENT_NOQUOTES: Converts neither single nor double quotes. |
Optional | Integer |
Return values:
The translation table as an array.
Value Type: Array.
Pictorial Presentation
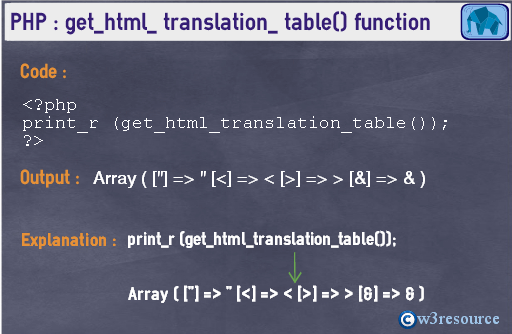
Example:
<?phpprint_r (get_html_translation_table());echo '<br>';print_r (get_html_translation_table(HTML_ENTITIES));echo '<br>';print_r (get_html_translation_table(HTML_SPECIALCHARS,ENT_QUOTES));?>
Output:
Array ( ["] => " [<] => < [>] => > [&] => & )
Array ( [ ] => [¡] => ¡ [¢] => ¢ [£] => £ [¤] => ¤ [¥] => ¥ [¦] => ¦ [§] => § [¨] => ¨ [©] => © [ª] => ª [«] => « [¬] => ¬ [] => [®] => ® [¯] => ¯ [°] => ° [±] => ± [²] => ² [³] => ³ [´] => ´ [µ] => µ [¶] => ¶ [·] => · [¸] => ¸ [¹] => ¹ [º] => º [»] => » [¼] => ¼ [½] => ½ [¾] => ¾ [¿] => ¿ [À] => À [Á] => Á [Â] => Â [Ã] => Ã [Ä] => Ä [Å] => Å [Æ] => Æ [Ç] => Ç [È] => È [É] => É [Ê] => Ê [Ë] => Ë [Ì] => Ì [Í] => Í [Î] => Î [Ï] => Ï [Ð] => Ð [Ñ] => Ñ [Ò] => Ò [Ó] => Ó [Ô] => Ô [Õ] => Õ [Ö] => Ö [×] => × [Ø] => Ø [Ù] => Ù [Ú] => Ú [Û] => Û [Ü] => Ü [Ý] => Ý [Þ] => Þ [ß] => ß [à] => à [á] => á [â] => â [ã] => ã [ä] => ä [å] => å [æ] => æ [ç] => ç [è] => è [é] => é [ê] => ê [ë] => ë [ì] => ì [í] => í [î] => î [ï] => ï [ð] => ð [ñ] => ñ [ò] => ò [ó] => ó [ô] => ô [õ] => õ [ö] => ö [÷] => ÷ [ø] => ø [ù] => ù [ú] => ú [û] => û [ü] => ü [ý] => ý [þ] => þ [ÿ] => ÿ ["] => " [<] => < [>] => > [&] => & )
Array ( ["] => " ['] => ' [<] => < [>] => > [&] => & )
View the example in the browser
See also
