PHP: strtr() function
PHP: Translate characters or replace substrings
The strtr() function is used to translate certain characters in a string.
Version:
(PHP 4 and above)
Syntax:
strtr(string_name, from_string, to_string)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| string_name | The string to be translated. | Required | String |
| from_string | Contains characters to be translated. | Required | String |
| to_string | Contains characters to be translated with. | Required | String |
Another Syntax:
strtr(string_namer, translating_array)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
Type |
| string_name | The string to be translated | Required | String |
| translating_array | Contains key value pairs. If values of the array elements are matched in the input string, then those characters in the input string are replaced with the corresponding keys of those values. | Required | Array |
Return value:
Returns the translated string.
Value Type: String.
Pictorial Presentation
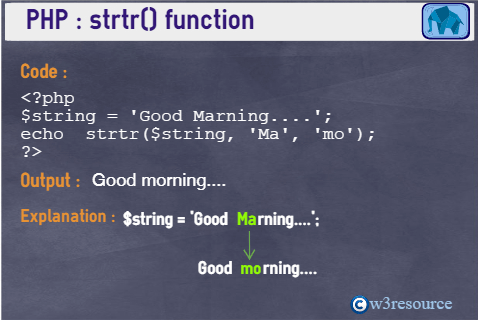
Example:
<?php
$string = 'Good Marning....';
echo strtr($string, 'Ma', 'mo');
?>
Output:
Good morning....
View the example in the browser
See also
Previous: strtoupper
Next: substr_compare
