PHP: vprintf() function
PHP: Output a formatted string
The vprintf() function is used to display array values as a formatted string.
Note. The function works as a printf() function but accepts an array as arguments.
Version:
(PHP 4 and above)
Syntax:
vprintf (format, array_args)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| format | Each conversion specification starts with a single percent sign (%) and ends with the following conversion characters.
% - returns a percent sign. b - the argument is treated as an integer and display it as a binary number. c - the argument is treated as an integer and display it as a an ASCII value. d - the argument is treated as an integer and display as a signed decimal number. e - the argument is treated as scientific notation (e.g. 1.2e+2). E - the argument treated as scientific notation (e.g.1.2E+2). u - the argument is treated as an integer, and display as an unsigned decimal number. f- the argument is treated as a float, and display as a floating-point number. (local aware) F - the argument is treated as a float, and display as a floating-point number (non-locale aware). g - shorter of %e and %f. G - shorter of %E and %f. o- the argument is treated as an integer, and display as an octal number. s - the argument is treated as string and display as a string. x - the argument is treated as an integer and display as a hexadecimal number (with lowercase letters). X - the argument is treated as an integer and display as a hexadecimal number (with uppercase letters). Optional specification : Sign specifier : display a sign (+ or -) in front a number. By default, a - sign is used in front of a number if it is negative. Padding character : Default character is space. An alternate padding character can be specified by prefixing it with a single quote. Alignment specifier. : - character makes the alignment left-justified. The default is right justified. Width specifier : An integer number specifies the width of the field. Precision specifier : The argument specifies how many decimal number should be displayed for floating numbers. When using this specifier on a string, it acts as a cutoff point, setting a maximum character limit to the string. |
Required | String |
| array_args | An array with an argument to be added as the first %-sign in the formatted string. | Required | Array |
Return value:
Returns the length of the outputted string.
Value Type: Integer.
Pictorial Presentation
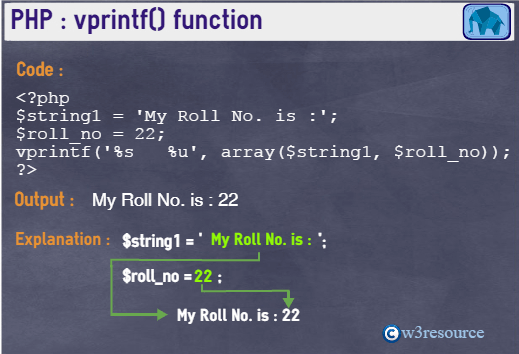
Example:
<?php
$string1 = 'My Roll No. is :';
$roll_no = 22;
vprintf('%s %u', array($string1, $roll_no));
?>
Output:
My Roll No. is : 22
View the example in the browser
See also
Previous: vfprintf
Next: wordwrap
