NumPy: numpy.tile() function
numpy.tile() function
The numpy.tile() function is used to construct an array by repeating a given array a certain number of times in a specified order. The order of repetition can be controlled using the 'reps' parameter.
If 'reps' has length d, the result will have dimension of max(d, A.ndim).
If A.ndim < d, A is promoted to be d-dimensional by prepending new axes. So a shape (3,) array is promoted to (1, 3) for 2-D replication, or shape (1, 1, 3) for 3-D replication. If this is not the desired behavior, promote A to d-dimensions manually before calling this function.
If A.ndim > d, reps is promoted to A.ndim by pre-pending 1’s to it. Thus for an A of shape (2, 3, 4, 5), a reps of (2, 2) is treated as (1, 1, 2, 2).
Note: Although tile may be used for broadcasting, it is strongly recommended to use numpy’s broadcasting operations and functions
The numpy.tile() function is useful in a variety of situations. For example, it can be used to create a larger dataset from a smaller one by repeating it multiple times, to generate a pattern of data, to create a matrix of repeating values, or to create a mosaic of images from a smaller image.
Syntax:
numpy.tile(A, reps)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| A | The input array. | Required |
| reps | The number of repetitions of A along each axis. | Required |
Return value:
c [ndarray] The tiled output array.
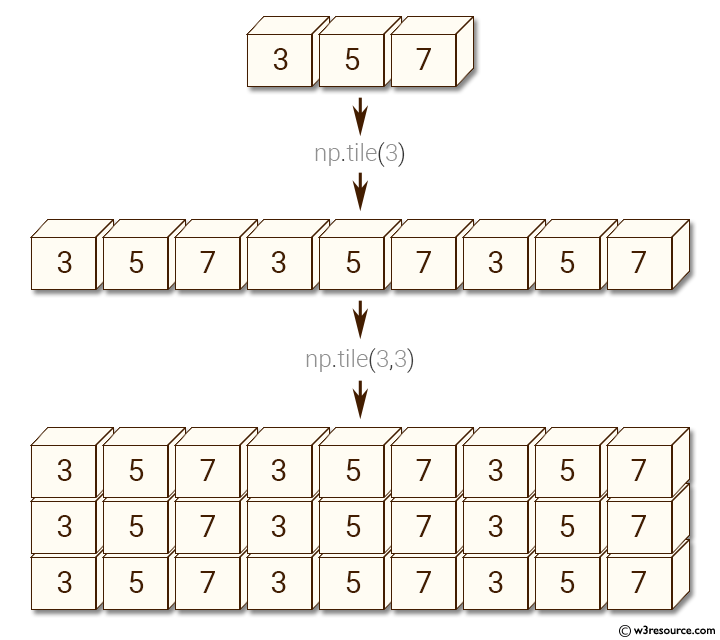
Example: Repeating an array using numpy.tile()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.array([3, 5, 7])
>>> np.tile(x, 3)
array([3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7])
>>> np.tile(x, (3,3))
array([[3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7],
[3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7],
[3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7]])
In the above code we first create a one-dimensional numpy array called "x" consisting of the values [3, 5, 7]. The numpy.tile() function is then used to repeat the array "x" along a specified axis.
In the first example, np.tile(x, 3), the array "x" is repeated three times along the first axis (i.e., the rows). The resulting array is [3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7].
In the second example, np.tile(x, (3,3)), the array "x" is repeated three times along the first axis and three times along the second axis (i.e., the columns). The resulting array is a 2D array with three rows and three columns, where each row is identical to the first example array [3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7].
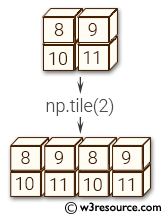
Pictorial Presentation:
Example: Replicating a 1D array multiple times along multiple dimensions using numpy.tile()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.array([3, 5, 7])
>>> np.tile(x, (3, 1, 3))
array([[[3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7]],
[[3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7]],
[[3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7, 3, 5, 7]]])
In the above code, we have specified (3, 1, 3) as the second argument, which means 'x' should be repeated 3 times along the first dimension, once along the second dimension, and 3 times along the third dimension.
The output of the numpy.tile() function is a new array with the specified dimensions, where 'x' has been replicated multiple times according to the specified pattern. The resulting array has a shape of (3, 1, 9), where the first dimension has a length of 3, the second dimension has a length of 1, and the third dimension has a length of 9.
Example: Tile a 2D array along axis 1 using numpy.tile()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> y = np.array([[3, 4], [5, 6]])
>>> np.tile(y, 3)
array([[3, 4, 3, 4, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 5, 6, 5, 6]])
In the above code we create a 2-dimensional array 'y' containing the values [[3, 4], [5, 6]]. Then, the np.tile() function is used to create a new array by repeating the values of 'y' 3 times along axis 1. The resulting array has shape (2,6).
Pictorial Presentation:
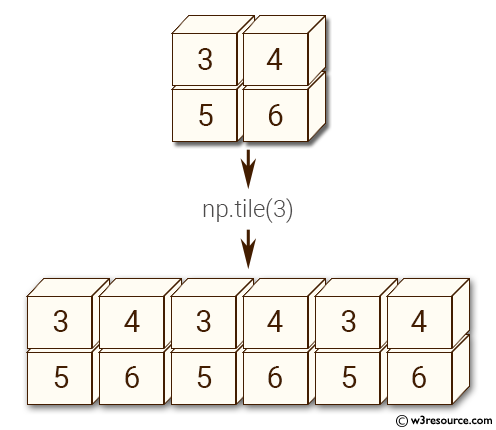
Example: Replicating and tiling arrays using numpy.tile()
>>> import numpy as mp
>>> np.tile(y, (3, 1))
array([[3, 4],
[5, 6],
[3, 4],
[5, 6],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]])
>>> z = np.array([3, 5, 7, 9])
>>> np.tile(z,(4,1))
array([[3, 5, 7, 9],
[3, 5, 7, 9],
[3, 5, 7, 9],
[3, 5, 7, 9]])
In the first example, the array "y" is tiled three times vertically using np.tile(y, (3, 1)), which creates a new array with three copies of "y" stacked vertically. The resulting array has six rows and two columns, with each row being a copy of "y".
In the second example, the array "z" is replicated four times vertically using np.tile(z, (4, 1)), which creates a new array with four copies of "z" stacked vertically. The resulting array has four rows and four columns, with each row being a copy of "z".
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
